Tags:androidarchitecture Related to:mobilehackingbug-bountysystemsecurity See also: Signatures in Android App Android Applications
Summary
An overview of Android system and security architecture
Android System Architecture Overview
- Android is based off linux
- FIle Permissons is based off linux permisson model
- Applications are isolated from each other by this permisson model
Dalvik vs Android runtime
-
dalvik was the first VM. no longer used it was replaced by android runtime
-
Android runtime trasnlates application bytecide to device instructions
-
Every app runs in its own sandboxed virtual machine similar to linux
Android IAM
-
separate user for an application(uid 10000 - 99999)
-
separate directory for an app
-
Apps communicate with each other via Content providers or Broadcast Recievers
-
Root level and system level users - full access
-
Emulators with gplay APIs dont allow root
-
Profiles
- Users
- Primary user - can only be removed with factory resets
- Secondary users - can be removed with primary users
- Guest Users
- Kid mode
- Work profile
- Users
Android System Architecture
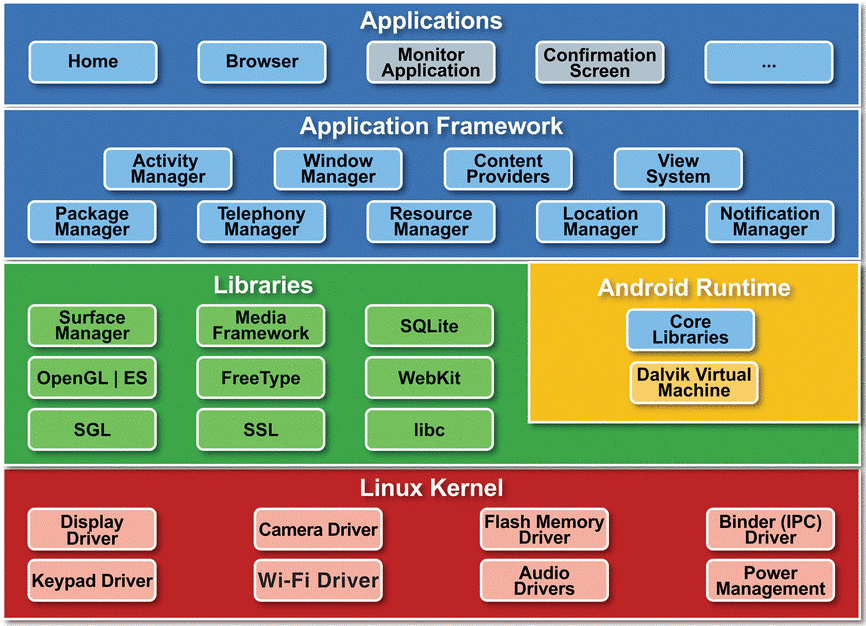 The lower level acts as an enabler for the upper level to function.
The lower level acts as an enabler for the upper level to function.
Linux Kernel
- SE Linux
- api / sdk version - higher the better but also needs more customers so some more lower versions are included
- Allows access to physical components via drivers
Hardware abstraction layer
- aids access to hardware by theapplication irrespective of manufacturer
- Can connect with external peripherals
Native C vs Android runtime
C and C++ are devices native language - doesnt require VM Devs prfer Java Now kotlin is offical std
Java API framework (APP framework)
- Content providers
- View System
- Mangers
- notification
- telephony
- pakage
- location
Application layer
- Pre installed apps
- contacts, phone, settings etc
- Google apps
- Vendor apps
Android Security and Signing
Application Signing
- Every Android app can be reverse engineered and modified - you get the byte code as apk which you convert to smalli and then to java
- How can you prevent anyone from signing an app and publishing in playstore?
- Public key cryptography
- App is signed by developers key then play store verifies it and signs with its key and publishes the app for the user
- keysign, jarsign, zip align
Secuirty Architecture
Follows a two tier model:
- Privilege model as in linux (Unique UID and GID)
- Permission model
- Defined in Android Manifest.xml by developer during development
- Cannot be changed later