Trusts
Tags:Active-Directorytrusts
Related to:crtp hackingoscp
See also: Enumeration Cheatsheet AD Introduction to Active Directory
Index: 🗂️ Index of CRTP
Summary
A brief overview of Trusts in AD
Trust
- In AD, trust is a relationship between two domains or forests which allow users of one domain or forest to access resources in the other
- Trusts can be
- Automatic - (parent-child, same forest etc)
- Established (forest, external)
- Trust Domain Objects(TDOs) represent these relationships in a domain
- Trusts are always established in the forest level.
Trust Direction
One-way: Unidirectional trust
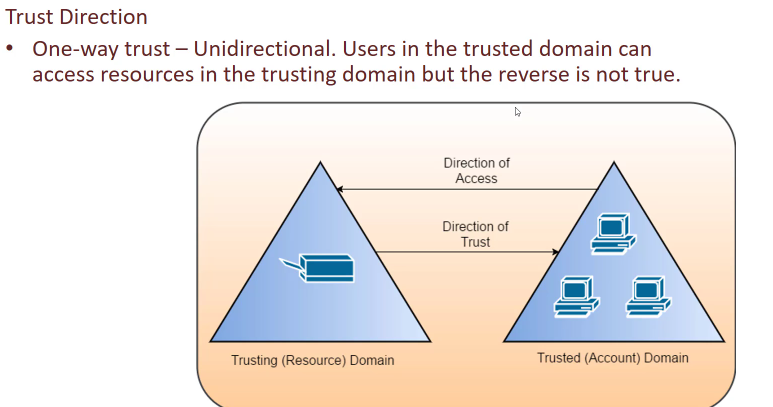 Direction of access is opposite to firection of trust
Direction of access is opposite to firection of trust
Two way: Bidirectional
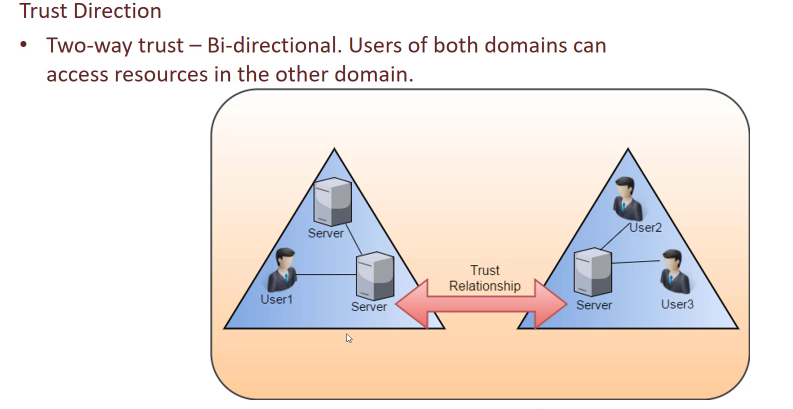 Note: Users must have enough privialges to access the resources
Note: Users must have enough privialges to access the resources
Trust transitivity
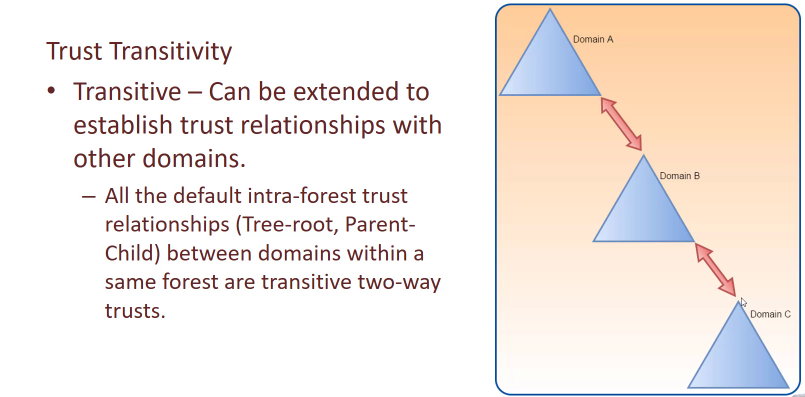 All default intra forest trust relationships between domains within a same forest are transitive 2 way trusts
All default intra forest trust relationships between domains within a same forest are transitive 2 way trusts
- Tree-root
- Parent-child
Non transitive - cannot be extended to other domains in forests can be oneway or two way
- Eg: Default trust (aka external trust) between two domains in different forests when forests do not have a trust relationship
Types Trust
-
Domain trusts
-
Default/Automatic trusts
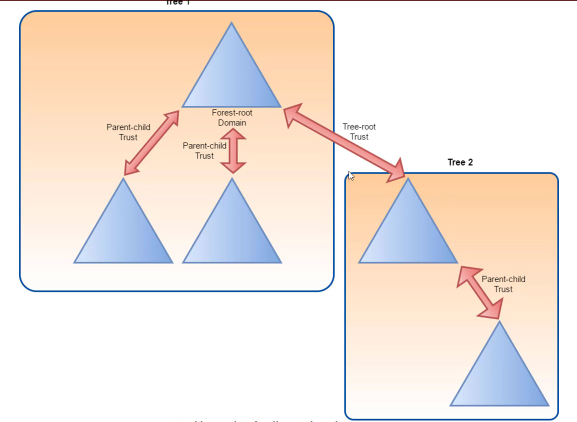
- Parent-Child trust : Created automatically between new domain and domain that preceeds in the namespace hierarchy, whenever a new domain is added in a tree. Always two way transitive
- Eg: dollarcorp.moneycorp.local is child of moneycorp.local
- Tree-root trust : created automatically when a new domain tree is added to a forest root. Always two way transitive
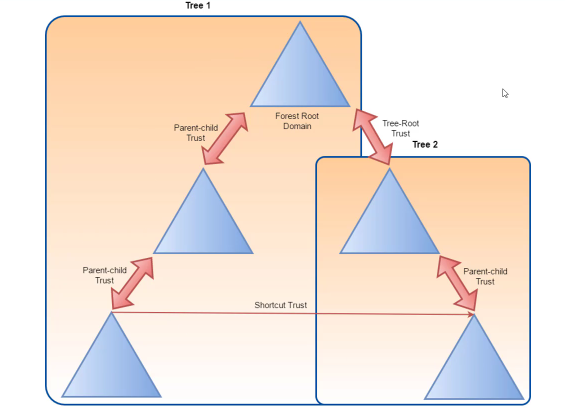
- Shortcut trust : manually established trusts in complex scenarios to reduce access time. Can be one way or two way transitive.
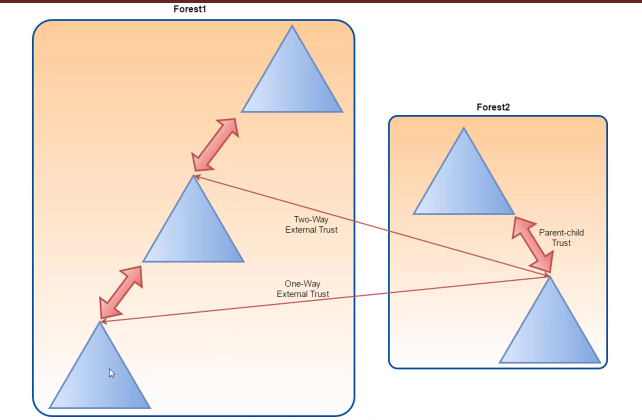
- External trusts : established between two domains in different forests which do not have a trust relationship. Can be one way or two way. It is non-transitive.
- Parent-Child trust : Created automatically between new domain and domain that preceeds in the namespace hierarchy, whenever a new domain is added in a tree. Always two way transitive
-
-
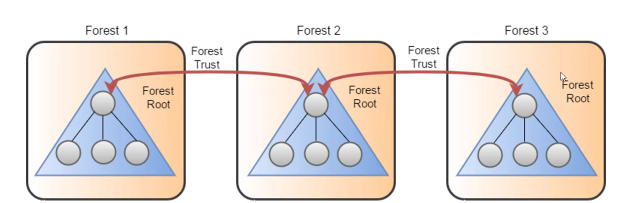
Forest Trusts
- Must be set manually
- Between forest root domains
- Cannot be extended to third forest (no implicit trust)
- Can be one way or two way and transitive (must be set manually) or non transitive
- In diagram below
- forest 1 trusts forest 2 bi directionally and
- forest 2 trusts forest 3 bi directionally.
- This doesnt necessarily imply forest 1 trusts forest 3